News Highlight
UNESCO to soon declare Visva-Bharati the world’s first living heritage university.
Key Takeaway
- It was a college until independence, and the institution was elevated to the status of Legislative University in 1951 by a central Act.
- Its first vice-chancellor was Rabindranath Tagore’s son.
- Furthermore, its second vice-chancellor was the grandfather of another Nobel Laureate economist, Amartya Sen.
Visva-Bharati University
- Overview
- It is a significant Central Government-funded independent university in Santiniketan, West Bengal, India.
- It is well-known in India as a prestigious Visual Arts practise and study centre.
- Rabindranath Tagore, a Nobel Prize winner, founded the university in 1921.
- Until the Visva-Bharati Society was registered as an organisation in May 1922, it was named after Nobel Laureate Rabindranath Tagore.
- A central Act granted the institution the status of a Central University in 1951.
- Its first vice-chancellor was Rabindranath Tagore’s son, and its second vice-chancellor was the grandfather of another Nobel Laureate economist, Amartya Sen.
UNESCO
- About
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) is a specialised United Nations (UN) organisation specified in a constitution signed on November 16, 1945.
- It encourages cooperation in education, research, and culture to foster peace worldwide.
- Headquarters
- Paris, France
- Member Countries
- It has 195 member countries, and it pursues its objectives through five major programs:
- Education
- Natural sciences
- Social and human sciences
- Culture
- Communication and Information.
- It has 195 member countries, and it pursues its objectives through five major programs:
- Reports Published
- Global Education Monitoring Report
- Gender Parity Index
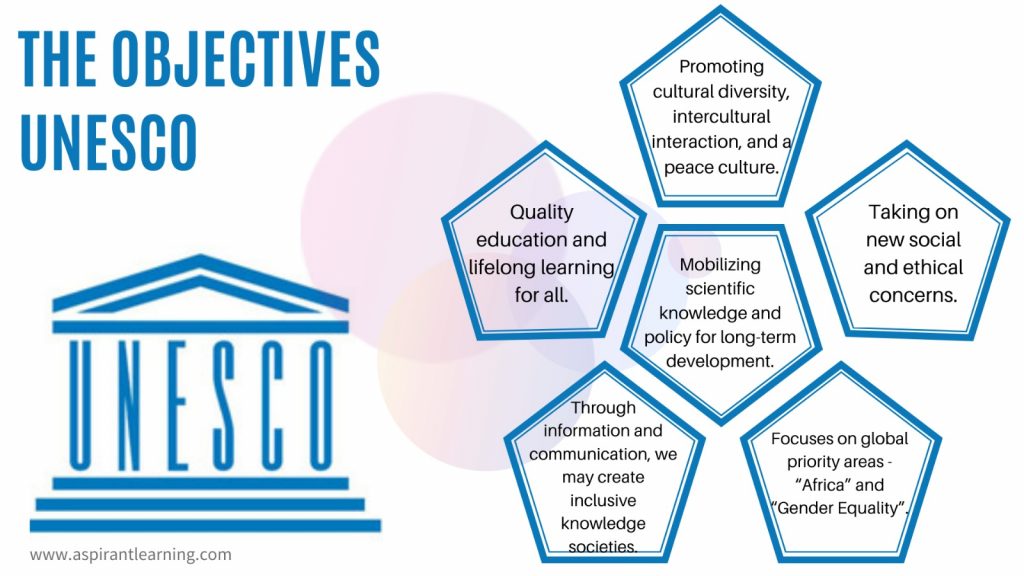
Functions of UNESCO
- It promotes peace via worldwide collaboration in education, science, and culture.
- UNESCO’s activities help to accomplish the Sustainable Development Goals outlined in Agenda 2030.
- The United Nations General Assembly adopted it in 2015.
- Its goal was to aid, support, and complement member countries‘ national efforts to eliminate illiteracy and provide free education.
- UNESCO also promotes the free exchange of ideas and knowledge by hosting conferences and providing clearinghouse and exchange services.
- UNESCO actively aims to safeguard the natural environment and humanity’s cultural legacy.
- In addition to supporting educational and scientific activities.
- UNESCO is well-known for its World Heritage Mission, encouraging countries worldwide to save natural and cultural heritage assets.
- UNESCO also oversees The Man and Biosphere Programme, which works to protect Biosphere reserves around the world.
UNESCO and India
- India is a founding member of UNESCO.
- The Indian National Commission for Cooperation (INCCU) with UNESCO is the name of India’s National Commission that works with UNESCO.
- The INCCU is part of the Ministry of Human Resource Development’s Department of Secondary and Higher Education.
- UNESCO has had a presence in India since 1948, with two offices.
- Since 1946, India has been re-elected to the UNESCO Executive Board.
- Members are elected for a tenure of four years.
- Every year, India makes significant financial contributions to the organisation.
- UNESCO’s most significant work in India is related to the country’s cultural heritage.
- In this regard, UNESCO collaborates closely with the Ministry of Culture.
The Area of Specialization of UNESCO
- Protecting Our Heritage and Fostering Creativity
- It is becoming increasingly clear that no progress can be long-term without a substantial cultural component.
- UNESCO has taken a three-pronged strategy to ensure that culture is given its proper position in developing policies and processes:
- Leads global advocacy for culture and development.
- Engages the international community to establish clear policy and legal frameworks.
- On the ground, works with governments and local partners to protect heritage, strengthen creative enterprises, and promote cultural pluralism.
- UNESCO agreements and international treaties to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural assets include:
- The Convention on the Protection and Promotion of the Diversity of Cultural Expressions (2005)
- The Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage (2003)
- The Universal Declaration on Cultural Diversity (2001)
- The Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage (2001)
- The Convention for the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage (1972)
- The Convention on the Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Traffic of Cultural Property (1970)
Pic Courtesy: Indian Express
Content Source: Indian Express



